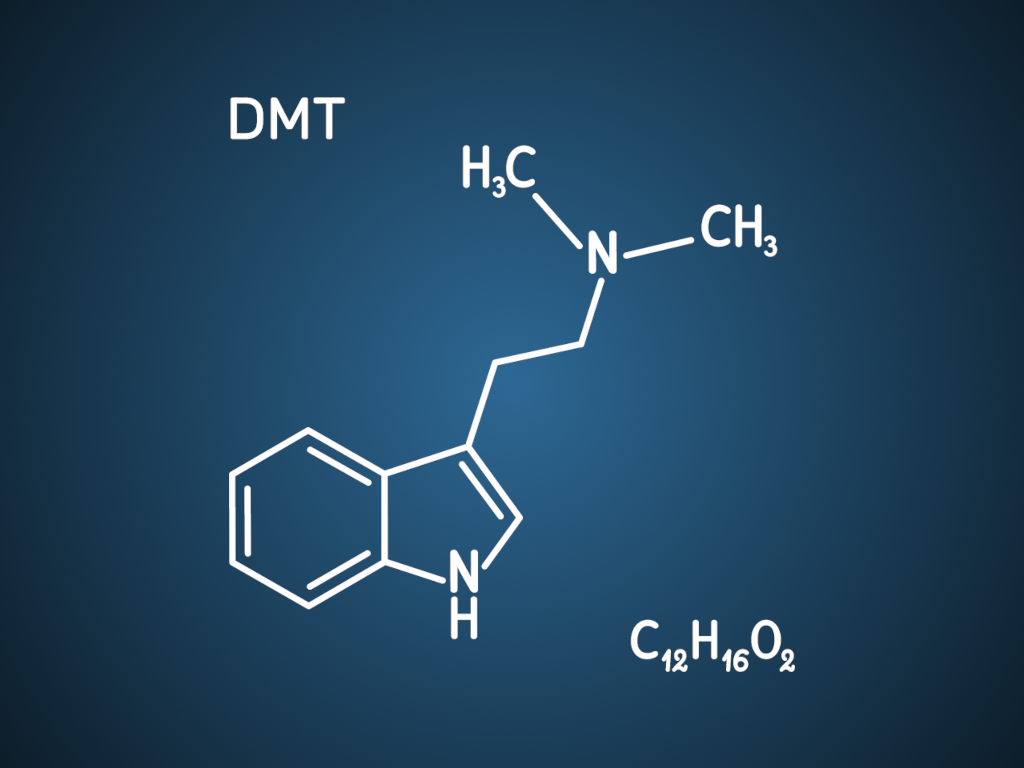
What is DMT? Dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is a strong hallucinogen, or psychedelic drug. Also known as dimitri, businessman’s special, the spirit molecule, changa, or fantasia. This powerful psychedelic has captured the attention of researchers, spiritual seekers, and the curious alike, resulting in both good and bad experiences.
This article will explore DMT, exploring its origins, effects, and potential applications. However, it’s crucial to approach this topic with caution. While DMT has been known to offer profound experiences, it’s also a potent hallucinogen that can lead to dependence.
We’ll also discuss the legal and ethical considerations surrounding its use, underscoring the need for responsible and informed decisions when it comes to substances like DMT.
Key Takeaways
- DMT is a naturally occurring hallucinogenic drug with spiritual and cultural significance in indigenous cultures.
- Different methods of consumption can produce different intensities and durations of effects, as well as potential risks and side effects.
- Treatment options are available to individuals seeking recovery from DMT dependence.
Understanding DMT: Origins and Forms
DMT, or n dimethyltryptamine dmt, is a naturally occurring hallucinogenic drug and a hallucinogenic tryptamine drug found in certain plants and animals, including tree barks and seeds. Sometimes referred to as the “spirit molecule,” DMT has been used for centuries in spiritual practices, particularly in South America, where it is a key component of the traditional Ayahuasca tea.
Typically found as a white crystalline powder, DMT can be extracted from natural sources and consumed in various ways, each with its unique effects and durations.
Natural Sources of DMT
DMT can be found in a variety of plants, including:
- Mimosa hostilis
- Psychotria viridis
- Myristicaceae
- Acacia trees
- Mimosa spp.
- Virola spp.
DMT (n dimethyltryptamine dmt) can be extracted from these plants through chemical processes. The Psychotria viridis plant, for example, is rich in DMT and can be processed using a polar extraction method.
These natural sources have been utilized by indigenous cultures for spiritual and healing purposes for centuries.
Extraction and Consumption Methods
Common methods of DMT consumption include:
- Smoking
- Vaporizing
- Snorting
- Injecting
- Drinking Ayahuasca tea
When ingested orally, DMT should be taken in combination with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), such as the Ayahuasca vine, to facilitate digestion and amplify its pharmacological effects. The intensity and duration of DMT’s effects can vary depending on the method of consumption.
For example, smoking or vaporizing DMT results in rapid, intense experiences that may last only 15 to 60 minutes, while drinking Ayahuasca tea leads to a slower onset and longer-lasting effects.
Cultural and Spiritual Significance
DMT has held a significant place in indigenous cultures for centuries, particularly in South America, where it is often used in spiritual and healing practices. The traditional Ayahuasca ceremony is a prime example of DMT’s cultural and spiritual significance, as the tea contains DMT as one of its primary active components. Participants in these ceremonies often report profound spiritual and transformative experiences, such as connecting with higher dimensions and encountering spiritual beings.
As a result, DMT’s use in these traditional contexts has garnered both respect and intrigue from people around the world.
The Science Behind DMT’s Effects
The powerful hallucinogenic effects of DMT stem from its interaction with serotonin receptors in the central nervous system, particularly the 5-HT2A receptor in the brain. As a result, DMT alters perception, mood, and cognition, inducing intense and often otherworldly experiences.
The specific mechanisms behind DMT’s hallucinations are still under investigation, but its effects on serotonin receptors play a crucial role in shaping these remarkable experiences.
Research is Showing DMT can Save Lives During Trauma
Research is indicating that endogenous psychedelics may function as neurotransmitters and could play a part in the growth, maintenance, repair, and protection of neurons in the brain. Pioneering work in the field demonstrated the existence of DMT in the pineal gland and visual cortex of the rat brain.
The human brain contains the enzyme and other factors necessary for the biosynthesis, storage, and release of DMT. Despite substantial evidence, it takes some time for these compounds to be accepted as neurotransmitters, particularly considering the history and misconceptions surrounding hallucinogens.
“The natural function of endogenous hallucinogens might be to protect neurons from hypoxia. If someone were to suffer a physical trauma, lose blood, and go into a hypoxic state, endogenous hallucinogens would help neurons survive while that individual did something to relieve the trauma. Going into a dissociative state may help people survive such circumstances.” Steven Barker, Louisiana State University
Serotonin Receptor Interaction
DMT binds to the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor as an agonist, exhibiting a high affinity for binding to the receptor. This interaction leads to significant modifications in perception, mood, and cognition. DMT has the ability to increase serotonin levels. This neurotransmitter is associated with feelings of happiness..
This activation of serotonin receptors contributes to the intense and often life-changing experiences that DMT users report, and it’s essential to be aware of the potential risk of serotonin syndrome.
Hallucinogenic Mechanisms
The exact mechanisms responsible for DMT’s hallucinogenic effects are still being explored, but it is believed that its ability to alter brain processes and sensory perception plays a significant role. For example, DMT has been observed to induce a pattern of cortical activity similar to that experienced during visual perception.
Additionally, the activation of the serotonin 2A (5-HT2A) receptor is thought to play a key role in generating the vivid and immersive hallucinations associated with DMT.
Duration and Intensity of Effects
The duration and intensity of a DMT experience can differ depending on factors such as the method of consumption and individual sensitivity. When smoked or vaporized, DMT effects have a rapid onset, often reaching peak intensity within minutes and subsiding within 30 to 45 minutes.
In contrast, when consumed orally as part of Ayahuasca, the onset of effects is slower, but the experience typically lasts longer, ranging from hours to even days in some cases. Regardless of the method, DMT experiences are renowned for their intensity, sometimes described as “breaking through” to an alternate reality or encountering otherworldly entities.
Physical and Psychological Consequences of DMT Use
While DMT can provide profound and transformative experiences, its use also carries potential risks and side effects, both short-term and long-term. It’s important to comprehend the impacts of DMT use before deciding whether to interact with this potent substance.
Short-Term Effects
Short-term effects of DMT can include:
- Increased heart rate
- Increased blood pressure
- Increased body temperature
- Visual and auditory hallucinations
- Dilated pupils
These effects can be distressing, particularly for individuals who are prone to anxiety or have pre-existing medical conditions. In some cases, DMT trips use may also lead to seizures, respiratory arrest, or even coma.
A bad trip can have a person feel like they are having near death experiences. Like other hallucinogens whether in a pure form or street drugs, more research on the physical effects, serotonin system, and psychological effects examining and comparing to the endogenous hallucinogen found in the brain.
Hence, using DMT requires caution and awareness of the possible hazards.
Long-Term Effects
The long-term effects of DMT use are not well-established but may include persistent psychosis and hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD). These conditions can cause individuals to experience ongoing hallucinations or other perceptual disturbances long after the acute effects of DMT have subsided.
Further research is needed to fully understand the potential long-term consequences of DMT use and its impact on mental health.
Is it DMT Addictive?
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse , it is unclear whether DMT is an addictive substance. Small studies suggest that it is unlikely to lead to a substance use disorder, but people may develop a tolerance, leading to increased consumption in the future.
Overuse of high doses of DMT can cause symptoms of addiction, such as withdrawal symptoms if you stop using it. If you use DMT in high doses and often you increase your tolerance. Tolerance could lead to taking more DMT to get the same effect.
Potential DMT withdrawal symptoms include: mood swings, apathy, depression, anxiety, fatigue, lack of motivation, apathy, agitation, irritability, and jitteriness. Most who experience these symptoms have a sense of craving.
Risks and Side Effects
DMT use carries certain risks and side effects, including the potential exacerbation of existing mental health conditions, such as anxiety and depression. Additionally, DMT may interact with other drugs or substances, increasing the risk of adverse events.
Being mindful of your mental health background and any possible contraindications before using DMT helps to mitigate these risks.
If you take DMT along with other drugs or prescription drugs for your mental health, this can change the serotonin levels in your brain. This change could cause bad side effects. Serotonin syndrome can cause a life-threatening drug reaction.
Psychedelics of all kinds affect everyone differently. Your height and weight and whether other drugs are taken will determine the effects.
Comparing DMT to Other Psychedelic Substances
DMT shares some similarities and differences with other psychedelic drugs, such as LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide) and psilocybin. Understanding these similarities and differences can provide a better understanding of the unique properties and effects of each substance.
DMT, LSD, and psilocybin all produce hallucinogenic effects but differ in their chemical structures, duration, and intensity of effects. DMT is more potent and has a shorter duration than LSD and psilocybin, typically lasting only 10 to 30 minutes.
While all three hallucinogenic drugs can alter perception and psychoactive effects, the specific visual and sensory distortions can be distinct with DMT being known for its intense, immersive hallucinations.
Taking DMT vs. LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide)
DMT’s effects are shorter-lasting and more intense than those of LSD. Both substances alter perception and cognition, but the intensity and duration of their effects differ, with DMT producing rapid, immersive experiences and LSD providing a longer-lasting, mind-altering experience.
DMT vs. Psilocybin (Magic Mushrooms)
DMT and psilocybin share some similarities in their effects, with both substances inducing vivid hallucinations and altered states of consciousness. However, DMT is more potent and has a shorter duration than the effects of psilocybin, which usually last 4 to 6 hours.
The experiences induced by DMT, psilocybin, and other psychedelic drugs can be transformative, but the intensity and duration of their effects can vary depending on individual factors and the method of consumption.
Legal Status of DMT
DMT is currently classified as an illegal Schedule I substance under state and federal law in the United States, making its recreational use and possession punishable by law. However, decriminalization efforts are underway in some regions, and harm reduction strategies as well as addiction treatment services can help minimize the risks associated with substance abuse, drug use, and mental health issues with taking DMT.
DMT in State and Federal Law
DMT is a Schedule I controlled substance in the United States, making it illegal for recreational use. Possession, sale, or manufacture of pure DMT or cut DMT can result in severe penalties, including incarceration and fines.
Despite its illegal status, DMT continues to be used by individuals seeking this naturally occurring substance trying to experience powerful and transformative effects.
Decriminalization Efforts
While DMT remains illegal at the federal level, some US cities have started to decriminalize the substance, with efforts like those in Oregon and Colorado decriminalizing certain psychedelic substances, including DMT. The City of Oakland, California, has also decriminalized a range of psychedelics, including DMT. These efforts reflect a growing interest in the potential therapeutic benefits of psychedelics and a shift in public perception about their use.
Recognizing and Addressing DMT Dependence
While DMT is not deemed physically addictive, it’s still important to identify and tackle any indications of dependence or misuse, including potential drug abuse. By identifying the signs of dependence, supporting loved ones, and exploring treatment options and resources, individuals can take steps to address DMT drug use and dependence.
Signs of Dependence
Signs of DMT dependence may include cravings, distress when not using, and changes in mood or behavior. While physical dependence on DMT is rare, individuals may still develop a substance use disorder related to its use, characterized by continued use despite adverse outcomes and an inability to fulfill commitments.
Recognizing these signs is crucial for addressing any problematic use and seeking appropriate support.
Supporting a Loved One
If you’re aware of someone battling DMT dependence, it’s important to handle the situation with empathy, comprehension, and open dialogue. Encourage your loved one to seek help and offer your support throughout their recovery journey.
By providing a safe and supportive environment, you can help your loved one overcome their dependence and work towards a healthier relationship with DMT.
Treatment Options and Resources
Treatment options for DMT dependence include detox, inpatient or outpatient programs, and support groups, with resources such as Turning Point of Tampa offering comprehensive care. Depending on the individual’s needs, different levels of care may be appropriate, ranging from intensive inpatient treatment to ongoing aftercare and support groups.
Individuals can address their DMT dependence, and mental health problems and misuse of other substances and initiate a path toward recovery by seeking professional help and considering treatment options.
Summary
In conclusion, DMT is a powerful substance with a rich history and profound effects on human consciousness. While its use can lead to transformative experiences, it is essential to be aware of the potential risks and consequences associated with DMT. By understanding the science behind its effects, the legal and ethical considerations, and the importance of harm reduction strategies, individuals can make informed decisions about whether to engage with this remarkable compound. As research into its therapeutic potential continues to unfold, the future prospects for DMT therapy remain an exciting and evolving frontier.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does DMT affect serotonin receptors in the brain?
DMT binds to serotonin 5-HT2A receptors in the brain, acting as an agonist and eliciting significant changes in perception, mood, and cognition.
What natural sources contain DMT?
DMT is naturally occurring in various plant species such as Mimosa hostilis and Psychotria viridis, which can be further processed to extract the chemical.
How does the duration of DMT effects compare to other psychedelics like LSD and magic mushrooms?
Compared to LSD and magic mushrooms, DMT has a shorter duration of effects, lasting for approximately 10-30 minutes.
What are some potential long-term effects of DMT use?
The potential long-term effects of DMT use include persistent psychosis and HPPD, though these have not been definitively established.
What treatment options are available for DMT dependence?
Treatment for DMT dependence includes detox, inpatient or outpatient programs, and support groups. Resources such as Turning Point of Tampa provide comprehensive care to help individuals manage their dependency.
Sources:
https://nida.nih.gov/research-topics/psychedelic-dissociative-drugs#drugs-safe
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0028390822002799
https://adf.org.au/drug-facts/dmt/
https://drugfree.org/drugs/what-is-dmt/
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnins.2016.00423/full